Vendor lifecycle management activities are siloed in most organizations, leading to poor coordination and collaboration across procurement, risk, legal, compliance, and finance departments. These silos significantly limit the efficiency and effectiveness of vendor management and the value it can create across the organization.
Establishing and implementing a robust vendor management framework is a game changer for addressing these challenges. It provides a blueprint for aligning the people, processes, and systems across all vendor lifecycle management activities so organizations can drive more value and less risk from critical vendor relationships.
In this blog post, I will walk you through understanding, implementing, and maximizing a vendor management framework that can be right-sized to your organization’s own goals and unique needs. Doing so will lay the foundation for a more streamlined and efficient vendor lifecycle management process within your organization.
Table of Contents
Defining the Vendor Lifecycle Management Framework
At its core, a vendor lifecycle management framework is a comprehensive blueprint for managing every stage of the vendor relationship – from initial selection to eventual offboarding. An effective vendor management framework encompasses more than just the activities associated with relationship maintenance. It also defines the governance necessary for vendor management to be effective and support organizational goals and objectives.
Let’s explore it in more detail.
What is a Strategic Vendor Management Framework?
A strategic vendor management framework provides guardrails and structure for managing vendor interactions throughout the vendor management lifecycle, enabling systematic and consistent management of performance, risk, costs, compliance, and other important aspects of vendor relationships.
The strategies, policies, and processes that guide vendor governance are key components of a robust vendor management framework. These ensure vendors meet the company’s standards for quality, security, compliance, and performance.
Critical Operational Areas to Include in the Framework
A well-structured vendor management framework aligns three critical operational areas that span the lifecycle of the vendor relationship: procurement operations, contract management operations, and third-party risk operations.
- Procurement Operations cover activities related to sourcing and acquiring goods and services from external suppliers, as well as ensuring selected vendors and systems align with organizational values and goals.
- Contract Management Operations incorporate activities associated with contracting and ongoing contract management, ensuring expectations for the relationship are clearly defined, and vendors perform up to expectations.
- Third-party Risk Management Operations tackle activities necessary to identify, mitigate, and manage third-party risk, ensuring proper safeguarding of organizational interests, compliance, and reputation.
By aligning procurement operations, contract management operations, and third-party risk operations within a comprehensive vendor management framework, organizations can optimize vendor relationships, mitigate risks, and drive sustainable business growth. This paves the way for an efficient, value-driven vendor management program.
The Advantages of an Effective Vendor Management Framework
There are many advantages to adopting a robust framework that improves efficiency and effectiveness across all phases of the vendor management lifecycle. Some of the most significant advantages include:
- Strategic Alignment. Aligning vendor management activities with organizational objectives and priorities is essential for driving strategic value. A vendor management framework facilitates alignment by prioritizing vendors that support strategic goals, optimizing resource allocation, and fostering innovation through collaboration with key suppliers. By integrating vendor management into broader business strategies, organizations can leverage vendor relationships as a competitive advantage and drive sustainable growth.
- Standardization and Consistency. Implementing a vendor management framework allows organizations to standardize processes, documentation, and communication channels across all vendor relationships. By establishing uniform guidelines for vendor selection, onboarding, and performance evaluation, organizations ensure consistency in operations and decision-making. This standardization not only enhances efficiency but also facilitates knowledge transfer and scalability, enabling organizations to replicate successful practices across different departments or business units.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration. A robust vendor management framework fosters clear and effective communication channels between cross-departmental stakeholders and external vendors. By facilitating regular dialogue, feedback exchange, and joint problem-solving, organizations can strengthen relationships and align objectives with vendor capabilities. Enhanced collaboration enables proactive risk management, timely issue resolution, and innovation co-creation, driving continuous improvement and value generation.
Enhanced Compliance Adherence. Adopting a vendor management framework ensures that vendors are selected and managed in accordance with regulatory requirements and industry standards. By aligning various compliance protocols, frameworks help to mitigate the risk of non-compliance penalties and reputational damage. Furthermore, standardized processes facilitate audit readiness and streamline compliance reporting, saving time and resources while strongly adhering to legal and regulatory frameworks.
Vendor Centric’s Proven Vendor Management Framework
Now that we’ve outlined the general concept of vendor management frameworks let’s take a look at what a modern, effective framework looks like.
Vendor Centric’s vendor management framework was developed in 2006 and is one of the first frameworks to incorporate procurement, contract, and third-party risk operations. Now in its third iteration, our framework incorporates the latest best practices and aligns with the most common regulatory standards for third-party management.
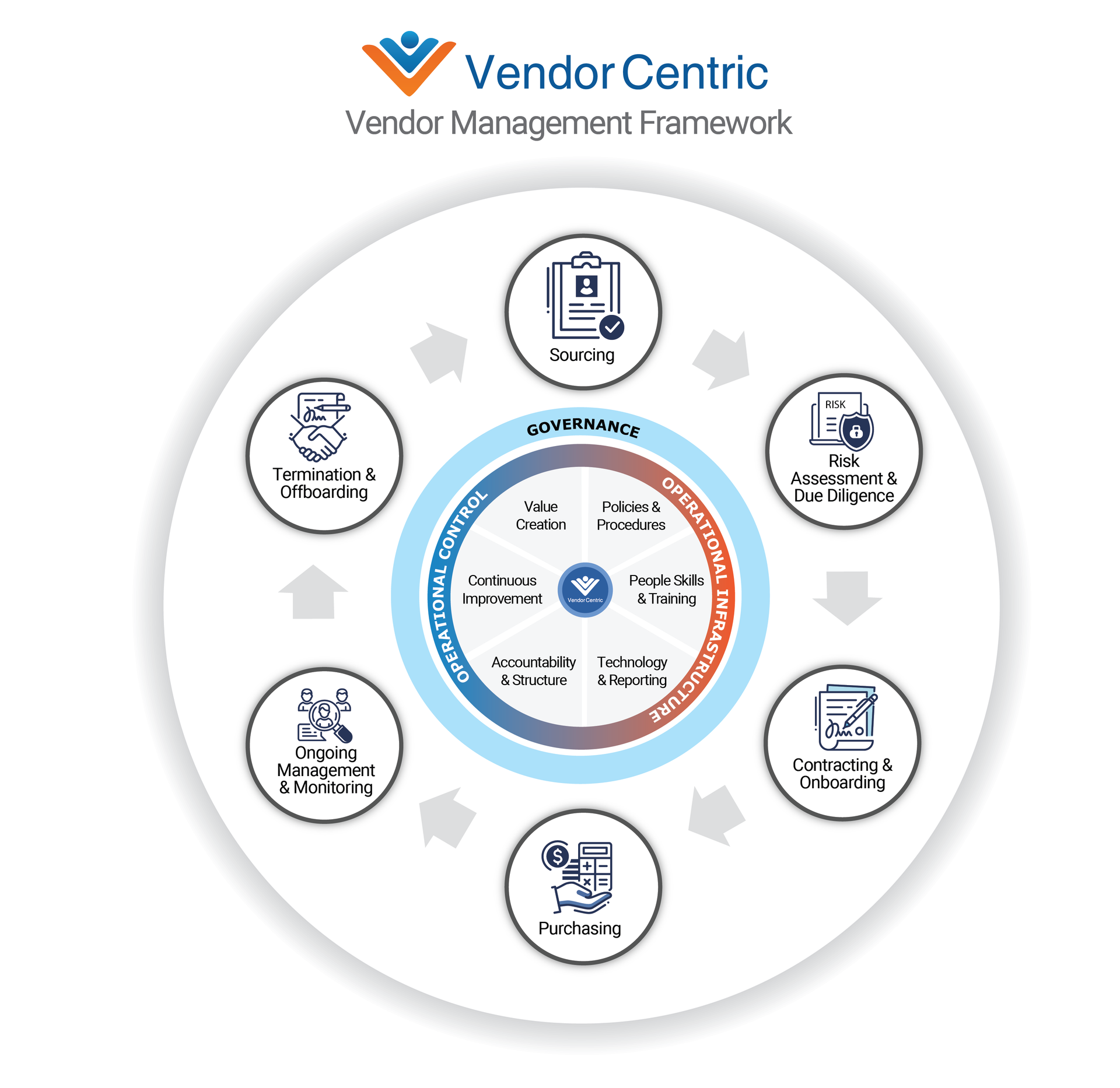
Our vendor framework is divided into two main sections. The outer ring focuses on the activities that must be managed through the vendor lifecycle (lifecycle stages). In contrast, the inner ring addresses critical components of vendor governance (governance structure) to ensure activities are aligned with organization goals and managed thoroughly and consistently.
Lifecycle Stages
- Sourcing activities ensure the right vendor(s) are identified and selected to meet corporate sourcing requirements.
- Risk Assessment and Due Diligence activities evaluate and mitigate potential risks before entering a contract.
- Contracting and Onboarding activities focus on negotiating high-value, low-risk contracts and integrate vendors into your operations.
- Purchasing activities ensure goods and services are acquired through efficient purchasing and spending control.
- Ongoing Management and Monitoring activities drive high vendor performance levels, control costs, and manage risk.
- Termination and Offboarding activities systematically end and de-risk the vendor relationship.
Governance Structure
- Policies and Procedures establish the overarching rules, guidelines, activities, and operational controls for vendor management.
- People, Skills, and Training ensure the right level of vendor management resources, subject matter expertise, and stakeholder knowledge.
- Technology and Reporting centralizes data, facilitates workflow, provides reporting, and ensures an audit trail of activities.
- Accountability and Structure defines the governing body and establishes the control structure to provide oversight and accountability.
- Continuous Improvement ensures operations are continuously improved for efficiency, scale, and alignment with changing business priorities and regulations.
- Value Creation aligns vendor management with strategic priorities and creates value through cost savings, risk reduction, performance improvement, and innovation.
The scope of your vendor management function should always scale to your organization’s requirements, size, and overall risk appetite. However, all components of the vendor management framework need to be in place for the function to be effective.
Implementing a Vendor Management Framework
Implementing a vendor management framework requires a systematic approach to ensure alignment with your organization’s goals and effective integration with existing processes, often spanning multiple departments.
Here is a three-step plan you can follow:
Step 1: Assessment and Planning
Begin by conducting a comprehensive assessment of your current vendor management practices, including procurement processes, contract management protocols, and risk management strategies, to define strategies and identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
Engaging key stakeholders from departments such as procurement, legal, finance, information security, compliance, and risk management will be important; this will allow you to gain diverse perspectives and foster buy-in for the initiative.
Based on the assessment findings, develop a clear roadmap for implementing the vendor management framework, including objectives, scope, priorities, timelines, and resources required.
Step 2: Policy and Procedure Development
Next, develop standardized policies, procedures, and guidelines that govern all aspects of vendor lifecycle management that will be in the scope for your program. Policies should align with your unique regulatory requirements, industry best practices, and organizational objectives.
A key outcome of this process will be establishing clear roles and responsibilities for individuals involved in vendor management activities, delineating accountability and decision-making authority.
Step 3: Technology Enablement
The third step is to implement technology solutions that facilitate the execution and automation of vendor management processes. This may include vendor management software (VMS), contract lifecycle management (CLM) systems, risk assessment tools, and other communication platforms. Select technology vendors that offer scalable, user-friendly solutions that integrate seamlessly with existing systems and workflows and ensure they provide comprehensive training and support to internal stakeholders.
Step 4: Stakeholder Training and Communication
Finally, you’ll need to develop and deploy a comprehensive training program to educate all key stakeholders on the new policies, procedures, and technology tools associated with the vendor management framework. Tailor training sessions to the specific needs and roles of different departments, ensuring that employees understand their responsibilities and how they contribute to the overall success of vendor management initiatives.
Investing in comprehensive training and communication efforts will empower your employees to adhere to the vendor management framework, driving sustainable results and value creation.
Leveraging Vendor Centric’s Vendor Management Framework to Maximize Success
A vendor lifecycle management framework is crucial to establishing a strategic, standardized vendor management program. It provides the blueprint for aligning people, processes, and systems organizationally, ultimately driving measurable value from your vendor management function.
At Vendor Centric, we’ve refined our vendor management methodology over the years to integrate current best practices and compliance standards while ensuring it works in the real world. Our modern framework can be tailored to organizations of all sizes and industries, ensuring your vendor management program is built on solid ground while also being right-sized for you.
Let’s discuss how Vendor Centric can help you implement a modern vendor management framework to get the most out of your vendor relationships.
2026 Framework Components for AI-Enabled Vendor Management
Modern vendor management frameworks must account for AI capabilities:
- AI-Powered Risk Assessment: Automated, continuous risk scoring and monitoring
- Intelligent Segmentation: AI-driven vendor categorization and tiering
- Automated Workflows: AI-enabled onboarding, assessment, and monitoring processes
- Predictive Analytics: AI forecasting vendor performance and risks
Frequently Asked Questions About Vendor Management Frameworks
What are the key components of a vendor management framework?
A comprehensive framework includes: governance structure (policies, roles, committees), vendor lifecycle processes (selection, onboarding, performance management, offboarding), risk management approach (assessment, monitoring, mitigation), technology enablement (platforms, tools, integrations), performance metrics and KPIs, continuous improvement mechanisms, and stakeholder engagement model. The framework should be documented, communicated, and regularly updated.
How long does it take to develop a vendor management framework?
Framework development typically takes 3-6 months: discovery and assessment (4-6 weeks) to understand current state and requirements, framework design (4-6 weeks) to define structure, processes, and policies, stakeholder review and refinement (2-4 weeks), and documentation and communication (2-4 weeks). Implementation takes an additional 6-12 months. Use a phased approach: start with core components, then enhance over time.
Should you build a framework from scratch or use a template?
Start with industry templates and frameworks (ISO 37001, COSO, NIST), then customize for your organization. Templates provide: proven structure and best practices, faster time to value, reduced risk of gaps, and easier stakeholder buy-in. Customize based on: industry requirements, organizational size and complexity, risk appetite, regulatory environment, and technology capabilities. Don’t reinvent the wheel—adapt proven frameworks to your needs.
Related Resources
Learn more about vendor management best practices:
Last Updated: January 5, 2026











 Tom is a trusted advisor on procurement and third-party management to organizations across the United States. Having worked with over 120 organizations over his 30-year career, he has a unique ability to bring creativity and discipline to finding solutions for even the most complex challenges his clients face.
Tom is a trusted advisor on procurement and third-party management to organizations across the United States. Having worked with over 120 organizations over his 30-year career, he has a unique ability to bring creativity and discipline to finding solutions for even the most complex challenges his clients face.



